lv hypertrabeculation This report summarizes the evidence concerning the etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical relevance of excessive trabeculation. Gaps in current knowledge of the clinical relevance of excessive trabeculation are indicated, with priorities .
10 best Scottish single malt whiskies to bless your home bar, tried and tested neat. From rich and full-bodied to fruity and sweet, wet your whistle with Scotland’s finestLearn about the best bottles of single malt scotch whisky that cost less than $100, from distillers like Bruichladdich, Laphroaig, The GlenDronach, and more. See more
0 · trabeculation of left ventricular myocardium
1 · symptoms of lv noncompaction
2 · prominent trabeculations on echo
3 · prominent lv trabeculations
4 · prominent left ventricular trabeculations
5 · lvnc cardiomyopathy symptoms
6 · left ventricular apical trabeculation
7 · hypertrabeculation of the left ventricle
The Glenlivet 25 Years Old. Finished in PX sherry and Cognac casks, this single malt has a deep amber hue and toffee and red fruit aromas. The complex palate .
Although excessive trabeculation is present, the presentation of ventricular dilatation, low EF, and nonischemic myocardial scar and genetic abnormality is the same as in dilated cardiomyopathy. Patient treatment is based on the . Left ventricular (LV) hypertrabeculation is defined by the presence of three or more trabeculations apically and up to the level of papillary muscles, seen in one echocardiographic view. 1 It can be distinguished from . Left ventricular (LV) hypertrabeculation is defined by the presence of three or more trabeculations apically and to the level of papillary muscles. Hypertrabeculation of LV .LV hypertrabeculation can occur either in isolation or in association with thickening (hypertrophy), enlargement (dilation) and / or reduced pumping ability of the heart. If you have LV hypertrabeculation, you will only be diagnosed .
Left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT) is a phenotype with multiple etiologies and variable clinical presentation and significance. It is characterized by a 2-layer myocardium .This report summarizes the evidence concerning the etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical relevance of excessive trabeculation. Gaps in current knowledge of the clinical relevance of excessive trabeculation are indicated, with priorities .Gaps in current knowledge of the clinical relevance of excessive trabeculation are indicated, with priorities suggested for future research and improved diagnosis in adults and children. Key .
The presence of excessive left ventricular (LV) trabeculation remains enigmatic: both seen on imaging in congenital, inherited, and acquired cardiomyopathies and in normal, healthy . If the phenotype is present in a patient with high pretest probability based on family history, symptoms, or imaging evidence of abnormal left ventricular size or function, we . Left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT) or noncompaction is a myocardial abnormality of unknown aetiology, frequently associated with monogenic disorders, particularly neuromuscular.
trabeculation of left ventricular myocardium
Left ventricular hypertrabeculation or noncompaction is a myocardial abnormality frequently associated with monogenic disorders, particularly neuromuscular disorders, or with chromosomal defects.For this abnormality, different synonyms are used such as spongy myocardium, LV noncompaction, and LV hypertrabeculation (LVHT). In this review it is stated that: (1) LVHT has a higher prevalence than previously thought and the prevalence of LVHT seems to increase with the improvement of cardiac imaging; (2) because LVHT is most frequently .Left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT) is a phenotype with multiple etiologies and variable clinical presentation and significance. It is characterized by a 2-layer myocardium with an enlarged trabecular layer and a thinner compacted layer. The prevalence has been increasing due to advances in c .
Background: Left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT), also known as noncompaction or spongy myocardium, is a cardiac abnormality of unknown etiology and pathogenesis frequently associated with genetic cardiac and noncardiac disorders, particularly genetic neuromuscular disease. This study aimed to review the current knowledge about the genetic or pathogenetic .Affiliations 1 a 2nd Medical Department with Cardiology and Intensive Care Medicine , Rudolfstifung Hospital , Vienna , Austria.; 2 b Rudolfstiftung Hospital , Danube University Krems , Vienna , Austria.
chanel ready to wear prices
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is characterized by prominent myocardial trabeculations and deep recesses. 1-3 The clinical spectrum of the disorder ranges from being completely asymptomatic to progressive left ventricular (LV) systolic impairment, a tendency to fatal arrhythmias and systemic thromboembolic events. 3 The . 1. Introduction. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is an unclassified cardiomyopathy characterized by an abnormally thick trabeculated non-compacted myocardial layer with adjacent deep intra-trabecular recesses and a thin compacted myocardial layer [].Although the underlying etiology of LVNC remains uncertain, emerging evidence suggests . Introduction. Left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is perceived as a rare genetic cardiomyopathy characterized by abnormal arrest of in-utero myocardial compaction ().Tertiary center cohorts of LVNC report association with life-threatening arrhythmias, thromboembolism, and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction (2–5).LVNC is . Hypertrabeculation vs Left Ventricular Noncompaction on Echocardiogram A Reason to Restrict Athletic Participation: 18M: Mumur: Observation: The patient returned to full athletic participation, and reevaluated annually. Ashraf Alazzoni, Vidhya Nair, et al: noncompaction reaction: 26M:
Adabifirouzjaei and colleagues proposed the valuation of the left ventricular function in patients in whom the hypertrabeculation was found on echocardiography or CMR . In patients with normal EF and no associated conditions, a family screening of first-degree relatives should be . A total of 154 patients (mean [SD] age, 57 [13.7] years; 31% female) who had undergone coronary angiography between 1995 and 2020 were included in the study.Distinguishing between pathologic LVNC and physiologic hypertrabeculation is a diagnostic challenge and is becoming increasingly commonplace with enhanced echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging modalities. Given the limited data on such patients, careful workup and discussion between patien .
Adabifirouzjaei and colleagues proposed the valuation of the left ventricular function in patients in whom the hypertrabeculation was found on echocardiography or CMR . In patients with normal EF and no associated conditions, a family screening of first-degree relatives should be performed.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, noncompacted trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer. It is characterized by prominent trabeculae, showing continuity between the deep trabecular recesses and the ventricular cavity. It has been . Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC), also known as non-compaction, noncompaction cardiomyopathy (NCCM), or left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT), is a myocardial abnormality morphologically characterised by an increased number of trabeculations distally to the papillary muscles of the left ventricle [1,2].Echocardiographic [3,4,5] and cardiac .Left ventricular (LV) hypertrabeculation is defined by the presence of three or more trabeculations apically and to the level of papillary muscles. Hypertrabeculation of LV can be a benign finding but can also be associated with left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. . (40%) with LV hypertrabeculation. We also identified 0, 1, and ≥2 VOIs in 72, 74, and 28 probands, respectively. More importantly, we found that the presence of an increasing number of VOIs in individual patients .
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a heart-muscle disorder characterized by prominent myocardial trabeculations and deep intertrabecular recesses in the LV cavity. LVNC is often diagnosed by echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, but a universally accepted definition of LVNC is lacking. Although the prevalence of LVNC in adults . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare myocardial disorder classified as a primary genetic cardiomyopathy by the American Heart Association in 2006 and as an unclassified cardiomyopathy by the European Society of Cardiology in 2008. . Left ventricular hypertrabeculation is not associated with cardiovascular morbity or mortality .
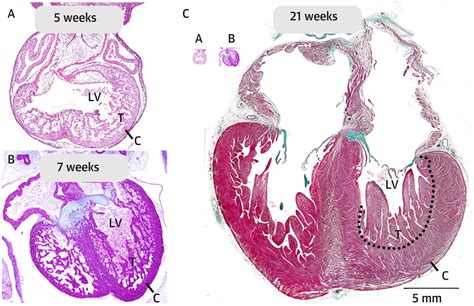
4.4 When to consider hypertrabeculation and LV non-compaction. An important differential diagnosis of LV fissures and outpouchings is LV non-compaction cardiomyopathy; a distinct cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by the presence of a two-layered myocardium with a prominent trabecular meshwork (Figure 6). LV non-compaction can also occur in . For this abnormality, different synonyms are used such as honeycombed myocardium, 3 spongy myocardium, 4 persisting myocardial sinusoids, 5 LV noncompaction, 6 isolated LV abnormal trabeculation, 7 and LV hypertrabeculation (LVHT). 8 Because this abnormality seems to be frequently overlooked 9, 10, 11 and because recently much progress .
Excessive trabeculation is a ventricular phenotype identified by imaging studies, most frequently echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR). 1 Similar to ventricular wall thickness or diameter, the presence of excessive trabeculation by itself does not define the presence of cardiomyopathy. As pointed out by Jenni, Oechslin, and colleagues, 2, 3 excessive .
INTRODUCTION. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [].LVNC was previously also called spongy myocardium or hypertrabeculation syndrome but these terms should not be used interchangeably with LVNC [].This review will focus on management of .
Left ventricular hypertrabeculation (LVHT), also termed “noncompaction,” is characterized by trabeculations in the inner layer of the myocardium and a thinner than usual external compact myocardial layer. INTRODUCTION. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy []) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [].LVNC was previously also called spongy myocardium or hypertrabeculation syndrome but these terms . The Stollberger criteria moved away from “isolated LVNC” to favour “LV hypertrabeculation (LVHT)”, aiming to include cases with additional cardiac anomalies and stipulated that (1) > 3 trabeculations protruding from the LV wall, apically to the papillary muscles, visible in one imaging plane and (2) perfusion of intertrabecular spaces .
symptoms of lv noncompaction
In both families, the 2 mutations/variants in LDB3 do not seem to cause LV dilation and dysfunction because carriers only show hypertrabeculation of the LV wall. Long-term follow-up will help to elucidate the role, if any, of this genetic variant and the evolving phenotypes of family members showing only LV wall hypertrabeculation.
michael kors ring rose gold
omega rental cars promo code
Purchase a certified pre-owned Rolex Datejust 16220 online at Bob's Watches. Free overnight shipping included. Shop today.
lv hypertrabeculation|prominent lv trabeculations