how to clone boot drive linux To clone a faulty or dying drive, run ddrescue twice. For the first round, copy every block without read error and map the errors to rescue.map. # ddrescue --force --no-scrape /dev/sd X /dev/sd .
Carry-On Allowance : 1 Bag. Each passenger is allowed to carry 1 piece of hand baggage. The dimensions should not exceed 20 cms x 40 cms x 55 cms and it should not weigh .
0 · making a cloned drive bootable
1 · how to clone bootable drive
2 · create bootable hard drive clone
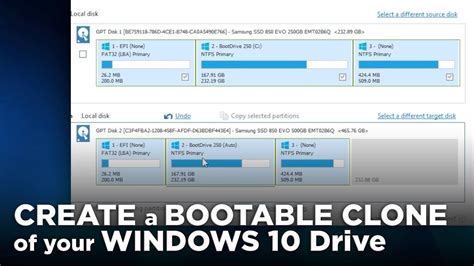
3 · create bootable clone windows 10
4 · clone bootable drive windows 10
5 · clone boot drive to larger
6 · clone a bootable hard drive
7 · bootable hard disk clone software
Somehow, looking at the current Rolex collection, we had the feeling that the Air-King was due an update. It was one of the last watches with a 31xx movement, and since the brand had . See more
making a cloned drive bootable
In this step-by-step guide, I’ll teach you how to efficiently clone drives on Linux using the excellent tools in your distro’s toolbox—like the venerable dd, the versatile .
Overview. As Linux users, we might want to clone or move our Linux installation from one device to another as it enables us to use an already configured setup on new .
The workhorse command for cloning on Linux is the venerable dd utility. dd has been around for decades and stands for "data duplicator". It copies raw data from inputs to . But the easiest one is to just copy all files from the old drive to the new one. Create an ext4 partition and a swap partition on the new drive. Boot from LiveUSB. Mount the old Ubuntu partition to some directory, mount the .
Download Live Linux USB Creator (Lili) from http://www.linuxliveusb.com/en/download. Create a bootable Clonezilla (Live Clonezilla) on .To clone a faulty or dying drive, run ddrescue twice. For the first round, copy every block without read error and map the errors to rescue.map. # ddrescue --force --no-scrape /dev/sd X /dev/sd .There are two common ways to boot a Linux system, MBR (an older method) or EFI (a newer method), and each have different partitioning requirements. If possible you’ll want to use EFI, . Backing up your hard drive is easy. Here are a few ways to clone your entire hard drive in Linux, allowing you to back up your data with ease.
how to clone bootable drive
Here are the top five solutions to clone a Linux hard disk drive: dd. Partimage. Partclone. Clonezilla. balenaEtcher. Some might come preinstalled with your Linux distro. Other Linux clone disk tools might be available to install from a third-party source. Either way, it shouldn't be long before you're able to get your system back up and running. 1) Installed Ubuntu Synaptic Package Manager - successful. 2) Installed Clonezilla via SPM - successful. 3) After installing Clonezilla on internal hard drive, it appears that Clonezilla must be downloaded and burned to a DVD. 4) Used Disks app to format USB external disk as Linux ext4 bootable. In this step-by-step guide, I’ll teach you how to efficiently clone drives on Linux using the excellent tools in your distro’s toolbox—like the venerable dd, the versatile Partimage, and the essential Clonezilla live CD. I’ll cover everything from basic commands up through advanced usage.
Overview. As Linux users, we might want to clone or move our Linux installation from one device to another as it enables us to use an already configured setup on new hardware. It also means that we can bypass the hassle of configuring a new system from scratch. The workhorse command for cloning on Linux is the venerable dd utility. dd has been around for decades and stands for "data duplicator". It copies raw data from inputs to outputs at the block level. While simple in concept, dd is immensely powerful and flexible once you understand it. Here is the basic syntax for the dd command: But the easiest one is to just copy all files from the old drive to the new one. Create an ext4 partition and a swap partition on the new drive. Boot from LiveUSB. Mount the old Ubuntu partition to some directory, mount the new one to some other directory.
Download Live Linux USB Creator (Lili) from http://www.linuxliveusb.com/en/download. Create a bootable Clonezilla (Live Clonezilla) on USB by running Live Linux USB Creator. Configure your Source desktop / laptop to .
To clone a faulty or dying drive, run ddrescue twice. For the first round, copy every block without read error and map the errors to rescue.map. # ddrescue --force --no-scrape /dev/sd X /dev/sd Y rescue.map. --force. This option is used when writing directly to a device (like a disk or partition).There are two common ways to boot a Linux system, MBR (an older method) or EFI (a newer method), and each have different partitioning requirements. If possible you’ll want to use EFI, but if you have an older machine that doesn’t support EFI mode you may need to use MBR. Backing up your hard drive is easy. Here are a few ways to clone your entire hard drive in Linux, allowing you to back up your data with ease.
Here are the top five solutions to clone a Linux hard disk drive: dd. Partimage. Partclone. Clonezilla. balenaEtcher. Some might come preinstalled with your Linux distro. Other Linux clone disk tools might be available to install from a third-party source. Either way, it shouldn't be long before you're able to get your system back up and running. 1) Installed Ubuntu Synaptic Package Manager - successful. 2) Installed Clonezilla via SPM - successful. 3) After installing Clonezilla on internal hard drive, it appears that Clonezilla must be downloaded and burned to a DVD. 4) Used Disks app to format USB external disk as Linux ext4 bootable.
In this step-by-step guide, I’ll teach you how to efficiently clone drives on Linux using the excellent tools in your distro’s toolbox—like the venerable dd, the versatile Partimage, and the essential Clonezilla live CD. I’ll cover everything from basic commands up through advanced usage. Overview. As Linux users, we might want to clone or move our Linux installation from one device to another as it enables us to use an already configured setup on new hardware. It also means that we can bypass the hassle of configuring a new system from scratch.
The workhorse command for cloning on Linux is the venerable dd utility. dd has been around for decades and stands for "data duplicator". It copies raw data from inputs to outputs at the block level. While simple in concept, dd is immensely powerful and flexible once you understand it. Here is the basic syntax for the dd command:
create bootable hard drive clone
But the easiest one is to just copy all files from the old drive to the new one. Create an ext4 partition and a swap partition on the new drive. Boot from LiveUSB. Mount the old Ubuntu partition to some directory, mount the new one to some other directory. Download Live Linux USB Creator (Lili) from http://www.linuxliveusb.com/en/download. Create a bootable Clonezilla (Live Clonezilla) on USB by running Live Linux USB Creator. Configure your Source desktop / laptop to .To clone a faulty or dying drive, run ddrescue twice. For the first round, copy every block without read error and map the errors to rescue.map. # ddrescue --force --no-scrape /dev/sd X /dev/sd Y rescue.map. --force. This option is used when writing directly to a device (like a disk or partition).
create bootable clone windows 10
givenchy mmw
Check-in online and save time at the airport. Online check-in is available from 24hrs prior departure.
how to clone boot drive linux|create bootable clone windows 10