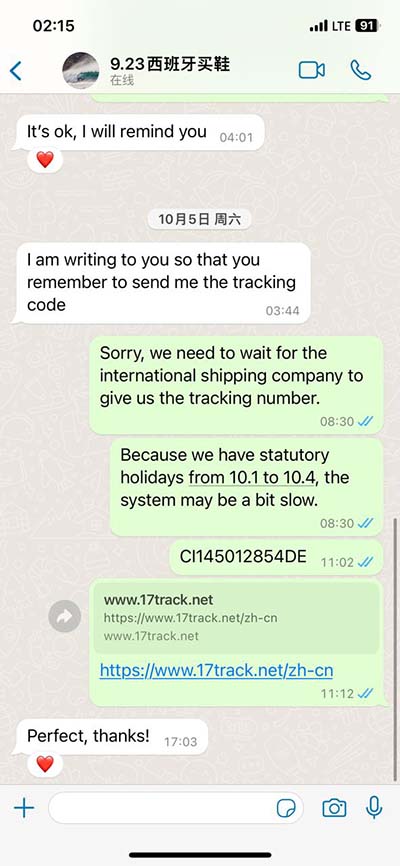
lvef 70% A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a .
Full list of Circle K Petrol Stations in Latvija | Circle K. List of stations. CIRCLE K ULMANIS 1. CIRCLE K KRASTA. CIRCLE K LIEPĀJA 1. CIRCLE K ZIEPNIEKKALNS. CIRCLE K ULMANIS 2. CIRCLE K IMANTA. CIRCLE K VENTSPILS.
0 · normal ejection fraction heart failure
1 · lvef edvi
2 · lv systolic function normal range
3 · lv ejection fraction sim
4 · left ventricular ejection fraction radiopaedia
5 · left ventricular ejection fraction lvef
6 · left ventricular ejection fraction echo
7 · hyperdynamic left ventricular function guidelines
1,179 Followers, 2,726 Following, 868 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Michael Upchurch (@church_lv)
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection . See moreAn EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, . See moreYour health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also referred to as diastolic heart . See moreYour health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used . See more
Ejection fraction measures the amount of blood the left ventricle of the heart pumps out to your body with each heartbeat. A healthy heart has an ejection fraction of 50% to 70%. A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 1 has persisted as the primary measure of left ventricular systolic function despite flaws in this approach. Patients with heart failure are relieved when the LVEF is reported . LVEF >70% compared with 1018 in the current study of clinical trial participants. 5 As noted previously, the authors have shown that there is no single LVEF for predicting . This activity reviews the calculation of LVEF, its clinical relevance and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in managing patients with depressed LVEF. Objectives: Identify the parameters required to calculate the . A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection .
For an ejection fraction in the range of 50% to 55%, most of the commonly used tests, if carefully performed, are accurate within a few percentage points (e.g. 55% plus or minus 3%). With respect to the lower limit of “normal” . An LVEF of 40% or less is referred to as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), formerly known as systolic heart failure, indicating an inability of the heart muscle to pump ("eject") enough blood during each . There was a 10-year age difference between individuals with LVEF ≤20% (mean age, 62 years) and those with LVEF >70% (mean age, 72 years). From a LVEF of 50% and greater, most patients were ages >70 years. From . Normal = LVEF 50% to 70% (midpoint 60%) Mild dysfunction = LVEF 40% to 49% (midpoint 45%) Moderate dysfunction = LVEF 30% to 39% (midpoint 35%) Severe dysfunction = LVEF less than 30%. Documentation may be quantitative (ejection fraction value) or qualitative (eg, "moderate dysfunction" or visually estimated ejection fraction).
The authors concluded any deviation in EF from the 60-65% range is associated with increased adjusted all-cause mortality. These results uncovered a new high-risk group: those with EF ≥ 70%. COMMENTARY. The most provocative finding in this study was that patients with EF ≥ 70% died at the same rate as patients with EF in the 35% to 40% range.
normal ejection fraction heart failure

lvef edvi
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been a key variable for the diagnosis and management of heart failure over the last three decades. The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for . LVEF ≥70%: adjusted HR 1.71 (95% CI 1.64-1.77) Deviation was "associated with poorer survival regardless of age, sex, or other relevant comorbidities such as heart failure," they concluded.

Normal ejection fraction (50% to 70%): Your heart is getting the job done! Mildly below normal (41% to 49%): Though you may not have symptoms, your heart has started to struggle to pump enough .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.It means that the left ventricle is very efficient and is pumping 70% of the total blood volume it contains OUT into the bloodstream. When the ejection fraction drops into the 50% range, it means the heart has been damaged by disease or a heart attack. When it drops into the 30% range, a patient could expect to be in some form of heart failure. Although the heart has two ventricles, it is the ejection fraction of the left ventricle—often referred to as LVEF (left ventricular ejection fraction)—cardiologists focus on when measuring ejection fraction. . 50% to 70%: Below normal: 41% to .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is an important predictor of mortality in patients with heart failure (HF) and is used to define many drug and device therapeutic indications. 1 – 8 Improvement in LV remodeling by neurohormonal inhibitor pharmacological therapy or cardiac resynchronization therapy is associated with improved survival and reduced .(any time in the past) LVEF assessment. may be quantitative (ejection fraction value) or qualitative (e .g , “moderate dysfunction” or visually estimated ejection fraction). Qualitative results should correspond to the numeric equivalents as follows: Hyperdynamic = LVEF greater than 70% Normal = LVEF 50% to 70% (midpoint 60%)heart (EF >70%). All examinations with significant LV hypertrophy or valve disease were excluded. The study included 16,994 subjects. A total of 720 subjects (4.2%) had a hyperdy- . European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging.5 LVEF was measured at rest and was assessed either by the Simp-son biplane method or qualitatively. Data on .
In a healthy 70-kilogram (150 lb) man, the stroke volume is approximately 70 mL, and the left ventricular end-diastolic volume (EDV) is approximately 120 mL, giving an estimated ejection fraction of 70 ⁄ 120, or 0.58 (58%).Healthy individuals typically have ejection fractions between 50% and 65%, [15] although the lower limits of normality are difficult to establish with confidence.Left ventricular (LV) systolic function is a powerful prognosticator of clinical outcome following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), 1, 2, 3 and patients who do not have in‐hospital LV ejection fraction (LVEF) assessment are less likely to receive evidence‐based therapy at discharge. 4, 5 The impact of PCI on LVEF and the association of LVEF evolution patterns . Mean age ranged from 61.6 to 69.4 years among patients with LVEF of less than 50% and between 71.2 and 71.8 years among patients with LVEF of greater than 50% (mean 10-year age difference between patients with LVEF ≤20% vs LVEF >70%, 62 vs 72 years). Patients with LVEF of less than 50% were predominantly men (ranging 62.2% to 80.7%) and .
Die linksventrikuläre Ejektionsfraktion (LVEF) ist ein Schlüsselwert für die Beurteilung der Herzfunktion. . 55% – 70% – normal; 40 – 54% – leichtgradig eingeschränkt; 35 -39% – mittelgradig eingeschränkt <35% – hochgradig eingeschränkt; In der Literatur finden Sie unterschiedliche Angaben für den Bereich zwischen 35 und 55 .The ejection fraction is one of the most common parameters used to diagnose heart failure. It refers to the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out during the systolic phase. Normal Ejection Fraction by Age is 55 to 65%. This may be one of the potential reasons why patients with an LVEF ≥ 70% are also prone to worsening EF. However, despite its importance, physicians are often unaware of the occurrence of early, modest worsening LVEF, which, thus, remains frequently unmanaged. Accordingly, it is necessary to regularly screen for early and modest worsening . lvef升高至70%以上时,死亡风险增加了73% . 这说明左室射血分数过高或过低都不好。 . 虽然lvef没有明显的降低,但患者的心脏也可能出现了心室收缩压降低、收缩和舒张功能储备减少等异常,也属于心力衰竭的一种。
Background—In asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, guidelines recommend left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of <50% as the threshold for referral for aortic valve replacement. We investigated the importance of LVEF on long-term outcome after aortic valve replacement in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with severe aortic .

lv systolic function normal range

chanel rumenilo
LV. Filmu katalogs. Filmas; Kino personas; Studijas . 2899 filmas Tiešsaistē publicētās filmas paredzētas tikai individuālai lietošanai. Publiskai demonstrēšanai nepieciešama tiesību īpašnieku – producentu, AKKA/LAA u.c. atļaujas.
lvef 70%|lvef edvi