omega 3 fatty acid structure Learn about the structure, sources, functions, and benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid. Find out how omega-3s are metabolized, absor. Fightshop, SIA +371 27794110 Bruņinieku 35-1, RĪGA, LV-1001
0 · omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
1 · omega 3 fatty acids examples
2 · omega 3 fatty acid transportation
3 · omega 3 fatty acid formula
4 · omega 3 fatty acid diagram
5 · omega 3 fatty acid chemistry
6 · omega 3 chemical name
7 · is omega 3 monounsaturated fat
After lv.100, you need 20311500 Exp to level up and same amount each level. For comparison, leveling up a servant lv.1 -> lv.100 needs 20311500 Exp, about 626 4* All Class Exp Card. So basically lv.100 -> lv.120 = leveling up 20 lv.100 servant. Image example how much the exp gauge gets filled if you use 20 x 5* all class exp cards on a .
Omega-3 (ω-3) fatty acids, renowned for their multiple health benefits, are pivotal in managing hyperlipidemia by modulating lipid profiles. .Learn about the structure, sources, functions, and benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid. Find out how omega-3s are metabolized, absor.
α-Linolenic acid, also known as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (from Greek alpha meaning "first" and linon meaning flax), is an n−3, or omega-3, essential fatty acid. ALA is found in many seeds and oils, including flaxseed, walnuts, chia, hemp, and many common vegetable oils. In terms of its structure, it is named all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid. In ph.Learn about the chemical structures and designations of omega-3 fatty acids, such as DHA, EPA, and ALA, and how they differ from omega-6 fatty acids. See examples of fatty acid structures .There are two main types of omega-3 fats that have essential roles in human health: EPA and DHA: Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) come mainly from cold . Together with our functional analyses and molecular dynamics simulations, this structure reveals details of how MFSD2A interacts with substrates and how Na + -dependent conformational changes.
In many livestock production systems, pasture and forage diets are common sources of omega-3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). Grain-based and feedlot diets are, instead, . Bottom line. Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of three important types of fat: ALA, DHA, and EPA. Getting enough of each type may help keep your retinas, brain, and other parts of your. Omega-3 fatty acids are “healthy fats” that may support your heart health. One key benefit is helping to lower your triglycerides. Specific types of omega-3s include DHA and EPA (found in seafood) and ALA (found in plants).
Another omega-3 fatty acid, whose biological activities are under investigation, is docosapentaenoic acid (DPA; designated 22:5). DPA can exist in both an omega-3 fatty acid form and an omega-6 fatty acid form. The .Figure 2: The structure of the fatty acids examined (A) These fats could not serve as essential fatty acids. . Any long chain omega-3 fatty acid has to originate from an omega-3 fatty acid from .Structure of Omega 3 Fatty Acid. The fatty acids have two ends, the carboxylic acid (-COOH) end, which is the beginning of the chain is known as “alpha”, and the methyl \(CH_3\) end, which the tail of the chain called “omega”.
omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 PUFAs) have been associated with several inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), and found to have an impact on gut microbiota. Docosahexaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid that is essential for neurological development and function, and it is supplied to the brain and eyes predominantly from dietary sources 1,2,3,4,5,6 .
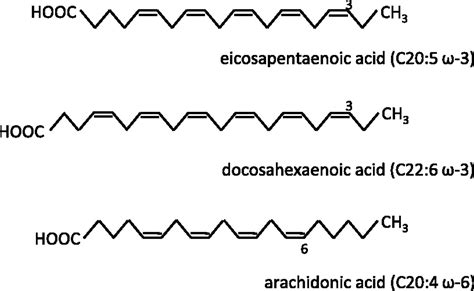
omega-3 fatty acids and their effects on human health. This fact sheet covers the current state of the science on these important compounds, as well as dietary recommendations and food sources of omega-3 fatty acids. FIGURE 1: Chemical Structure of Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a Type of Omega-3 Fatty Acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): This 20-carbon fatty acid’s main function is to produce chemicals called eicosanoids, which help reduce inflammation. EPA may also help reduce symptoms of depression .
The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are found in fish and other seafood.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega−3 fatty acid.In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n−3).It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid.In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and five cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end.α-Linolenic acid, also known as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (from Greek alpha meaning "first" and linon meaning flax), is an n−3, or omega-3, essential fatty acid.ALA is found in many seeds and oils, including flaxseed, walnuts, chia, hemp, and many common vegetable oils.. In terms of its structure, it is named all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid. [2]Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The Structure of Saturated Fatty Acids. (a) There is a zigzag pattern formed by the carbon-to-carbon single bonds in the ball-and-stick model of a palmitic acid molecule. (b) A space-filling model of palmitic acid shows the overall straightness of a saturated fatty acid molecule.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat found in animal oils and some plants, known for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to lower blood triglycerides. . DHA and EPA are the two omega-3 fatty acid compounds. The structure of DHA has a carboxylic acid group along with 22 carbon chains and 6 cis double bonds. With respect to the . Saturated fatty acids contain all carbon-carbon single bonds. This causes the molecules to form straight chains, as shown in the figure 11.1.2. Palmitic acid is an example of a saturated fatty acid. The hydrocarbon tails of saturated fatty acids are able to be packed together very tightly with one another, interacting through London forces.Omega-3s are found in oily fish. We have drastically reduced our intake of fish during the last century. Many of us therefore suffer from a deficiency of omega-3s, which has consequences for health. In this review, we focus on structure-functional relationships and the .
Background In recent years, public awareness of healthy diets has significantly increased, leading to a rise in the consumption of nutritional supplements. Among these, omega-3 fatty acids have become particularly popular. n − 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are widely distributed in marine and terrestrial environments. The primary sources of marine n − 3 . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The Structure of Saturated Fatty Acids. (a) There is a zigzag pattern formed by the carbon-to-carbon single bonds in the ball-and-stick model of a palmitic acid molecule. (b) A space-filling model of . What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids? Omega-3 fatty acids are components of fats in foods we eat. The term omega and number three refer to the chemical structure of the fatty acid. There are three main omega-3 fatty acids: 1. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the most common omega-3 fatty acid in the western diet. It comes from plants, and is found in .
Abstract. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are n‐3 fatty acids found in oily fish and fish oil supplements. These fatty acids are able to inhibit partly a number of aspects of inflammation including leucocyte chemotaxis, adhesion molecule expression and leucocyte‐endothelial adhesive interactions, production of eicosanoids like prostaglandins and . This distinction in structure leads to the three main types of fats: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. Saturated fatty acids (like palmitic and stearic acid) contain no carbon double bonds, monounsaturated (e.g., omega-9 fatty acids) have one, and polyunsaturated (aka PUFAs like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids) have more than one.Omega-3 fatty acids are found in foods, such as fish and flaxseed, and in dietary supplements, such as fish oil. The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils
In this Chemistry article, we will look into the omega-3 fatty acid’s structure, sources, benefits, uses side effects, symptoms, and importance in detail. Omega-3 Fatty Acid. A class of essential fatty acids known as omega-3s plays crucial roles in our body and may have a range of positive health effects. Omega-3 fatty acids are a crucial .Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega−3 fatty acid that is an important component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina.It is given the fatty acid notation 22:6(n−3). [1] It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fatty fish, fish oil, or algae oil. [1] [2] The consumption of DHA (e.g., from fatty fish such as .
The destruction of TAG structure and liberation of FAs allows absorption and transport in the bloodstream to the tissues where they are incorporated in their structure. . Sonnweber T., Weiss G., Tancevski I. The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Setting of Coronary Artery Disease and COPD: A Review. Nutrients. 2018;10:1864. doi: 10.3390 .Keywords: fatty acids, epa, dha, pufas, mental health, brain, omega. Introduction and background. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are fatty acids whose chemical structure is double-bonded with three atoms in the opposite direction to the methyl group . They are an essential component in lipid biotransformation in mammals.
There are three types of omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Of the three, EPA appears to be the most beneficial for .
omega 3 fatty acids examples
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (ω-3 Fatty Acids) Omega-3 fatty acids, also known as n-3s, mean the carbon-carbon double bond is present between the third and fourth end carbon atoms. There are two ends in fatty acids: carboxylic acid (COOH) alpha end-initial of the chain and methyl (CH3) omega end-tail of the chain.
These are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are called omega-3 because the third carbon from the end of the hydrocarbon chain is connected to its neighboring carbon by a double bond. Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\): Alpha-linolenic acid is an example of an omega-3 fatty acid. It has three cis double bonds and, as a result, a curved shape. For clarity .
large wide frame eyeglasses
adidas sneaker sokken heren
rolex datejust 41 arabic dial
omega 3 fatty acid transportation
220.lv e-veikals ir īsts tirdzniecības centrs internetā. Piedāvājam plašu preču izvēli par super cenām! Izdevīgi piegādes un apmaksas nosacījumi. Ienāciet!
omega 3 fatty acid structure|omega 3 fatty acid transportation